Introduction:
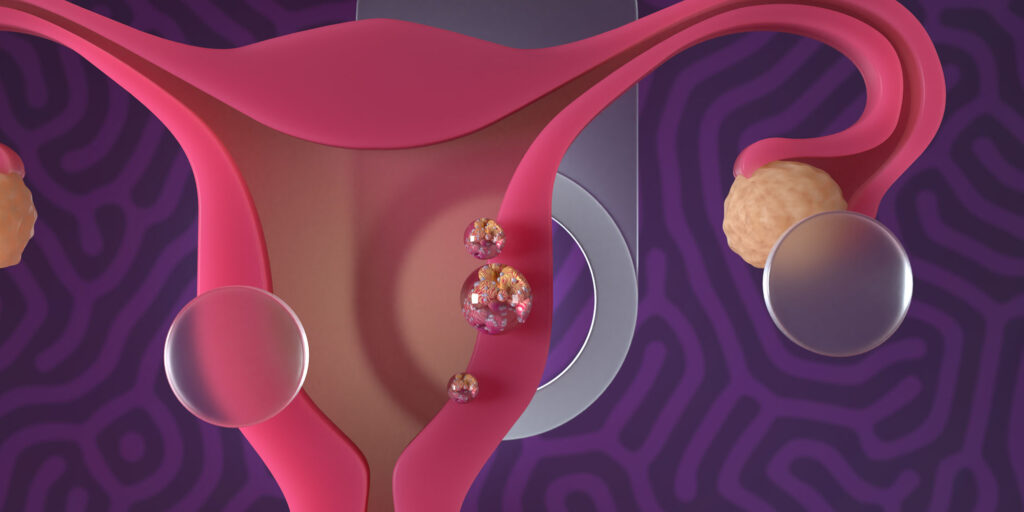
Endometrial cancer, also known as uterine cancer, is a type of cancer that originates in the lining of the uterus, called the endometrium. It is one of the most common gynecological cancers affecting women worldwide. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for endometrial cancer is crucial for early detection and effective management. In this blog post, we will delve into the various aspects of endometrial cancer, including its causes, symptoms, and available treatments.
Causes of Endometrial Cancer:
Endometrial cancer typically develops when cells in the endometrium mutate and grow uncontrollably. While the exact cause of these mutations is not always clear, several risk factors have been identified:
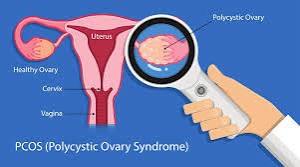
- Hormonal Imbalance: Fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly estrogen, can increase the risk of endometrial cancer. Conditions such as obesity, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can lead to hormonal imbalances, thereby raising the risk of developing endometrial cancer.
- Age: Endometrial cancer is more common in postmenopausal women, especially those over the age of 50. This is because estrogen levels tend to decline after menopause, and the risk of developing endometrial cancer increases with age.
- Obesity: Obesity is strongly associated with an increased risk of endometrial cancer. Excess fat tissue can lead to higher levels of estrogen in the body, which can promote the growth of cancerous cells in the endometrium.
- Diabetes: Women with diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes, are at a higher risk of developing endometrial cancer. Insulin resistance and elevated insulin levels may contribute to the development of cancerous cells in the endometrium.
- Genetic Factors: In some cases, endometrial cancer may run in families due to inherited genetic mutations, such as Lynch syndrome or hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC).
Symptoms of Endometrial Cancer:
Early detection of endometrial cancer is key to successful treatment. However, the symptoms of endometrial cancer can often be subtle or mistaken for other gynecological conditions. Common symptoms of endometrial cancer include:
- Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding: The most common symptom of endometrial cancer is abnormal vaginal bleeding, such as bleeding between periods, prolonged periods, or postmenopausal bleeding.
- Pelvic Pain or Pressure: Some women with endometrial cancer may experience pelvic pain or pressure, especially if the cancer has spread to nearby tissues or organs.
- Changes in Urinary or Bowel Habits: Endometrial cancer can cause changes in urinary or bowel habits, such as frequent urination, difficulty urinating, constipation, or diarrhea.
- Pain During Intercourse: Pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia) can be a symptom of endometrial cancer, especially if the cancer has spread to the surrounding tissues.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: In advanced cases of endometrial cancer, unexplained weight loss may occur due to a combination of factors, including loss of appetite and metabolic changes.
Treatment Options for Endometrial Cancer:
The treatment approach for endometrial cancer depends on several factors, including the stage of the cancer, the patient’s overall health, and their preferences. Treatment options may include:
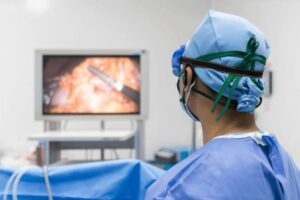
- Surgery: The primary treatment for endometrial cancer is often surgery to remove the uterus (hysterectomy) and, in some cases, surrounding tissues or lymph nodes. Minimally invasive techniques, such as laparoscopic or robotic-assisted surgery, may be used to reduce recovery time and complications.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy X-rays or other forms of radiation to destroy cancer cells or shrink tumors. It may be used before or after surgery, or in combination with other treatments to target remaining cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves the use of powerful drugs to kill cancer cells or prevent them from growing and dividing. It may be recommended for women with advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer, either alone or in combination with surgery and radiation therapy.
- Hormone Therapy: Hormone therapy may be used to treat endometrial cancer in women who cannot undergo surgery or have hormone-sensitive tumors. This treatment aims to block the effects of estrogen on cancer cells or lower estrogen levels in the body.
- Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapy uses drugs or other substances to target specific molecules involved in the growth and spread of cancer cells. It may be used in combination with other treatments for advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer.
Conclusion:
Endometrial cancer is a serious condition that requires prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for endometrial cancer, women can take proactive steps to protect their health and well-being. If you experience any symptoms of endometrial cancer or have concerns about your risk factors, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and guidance. Dr. Aneeta Talwar, a Consultant Obstetrics & Gynecology Laparoscopic & Endoscopic Gyn Surgeon in Bangalore, can provide expert care and personalized treatment